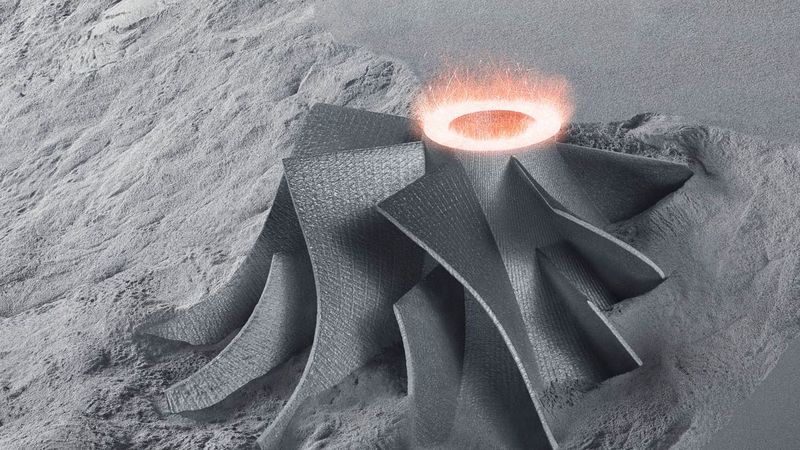
Additive manufacturing
Components, no matter what shape they have. Prototypes, unique items, and small and large series. Additive manufacturing is shaping the future of the manufacturing industry like hardly any other process. Additive manufacturing and/or laser sintering or laser melting can be used to manufacture, coat or repair components with extremely high material requirements. Compared with traditional, ablative manufacturing methods such as turning or milling, in additive manufacturing the design determines manufacturing. This is why it is referred to as "design for additive manufacturing" (DfAM).
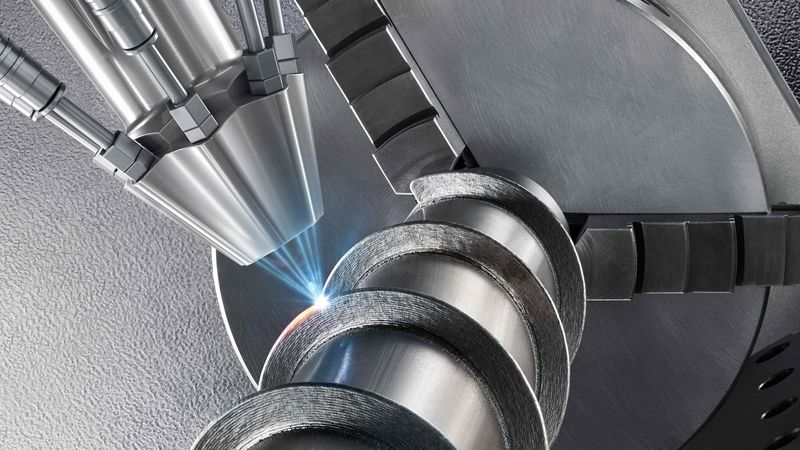
TRUMPF has brought two additive manufacturing laser processes to industrial maturity in the last 20 years which can be used to create complex shapes and individual metal components layer-by-layer from metal powder quickly, with flexibility, and cheaply: Laser metal fusion and laser metal deposition. As a pioneer in additive manufacturing methods, TRUMPF provides complete solutions with machines, beam sources, and services – all of which they have developed and produced themselves. This provides a clear competitive advantage to customers.
In additive manufacturing, there are no limits when it comes to design – even functions that are not feasible with conventional manufacturing methods can be integrated or complete assemblies can be constructed in one go.
The desired components and shapes are created precisely using only the material that is actually required with additive manufacturing.
Customized solutions and personalized components can be realized easily and with flexibility using additive manufacturing – even in series production.
Since no tools are required for additive manufacturing, you can work more cheaply and reduce both wear and setup times.
The high level of stability of complex structures and low weight of additively manufactured components make the process particularly attractive for lightweight design.
Which application examples are there for additive manufacturing?
- Creation of a personalized cranial implant or construction of dental crowns and bridges (LMF)
- Additive manufacturing of heat exchangers with extremely fine lattice structures (LMF)
- Coating of a maize chopper in order to improve the service life (LMD)
- Repair of a compressor blade after wear (LMD)
How are the additive manufacturing processes different?
An increasing number of variants, increasingly small lot sizes – the trend in many manufacturing industries is clear. Laser metal fusion (LMF) and laser metal deposition (LMD) are the two laser-based processes that take on these challenges and make additive manufacturing more and more attractive for industrial use. However, how are the processes different technically and which technology is precisely suited to which fields of application?
We would be pleased to advise you
Our additive manufacturing experts will be happy to advise you.