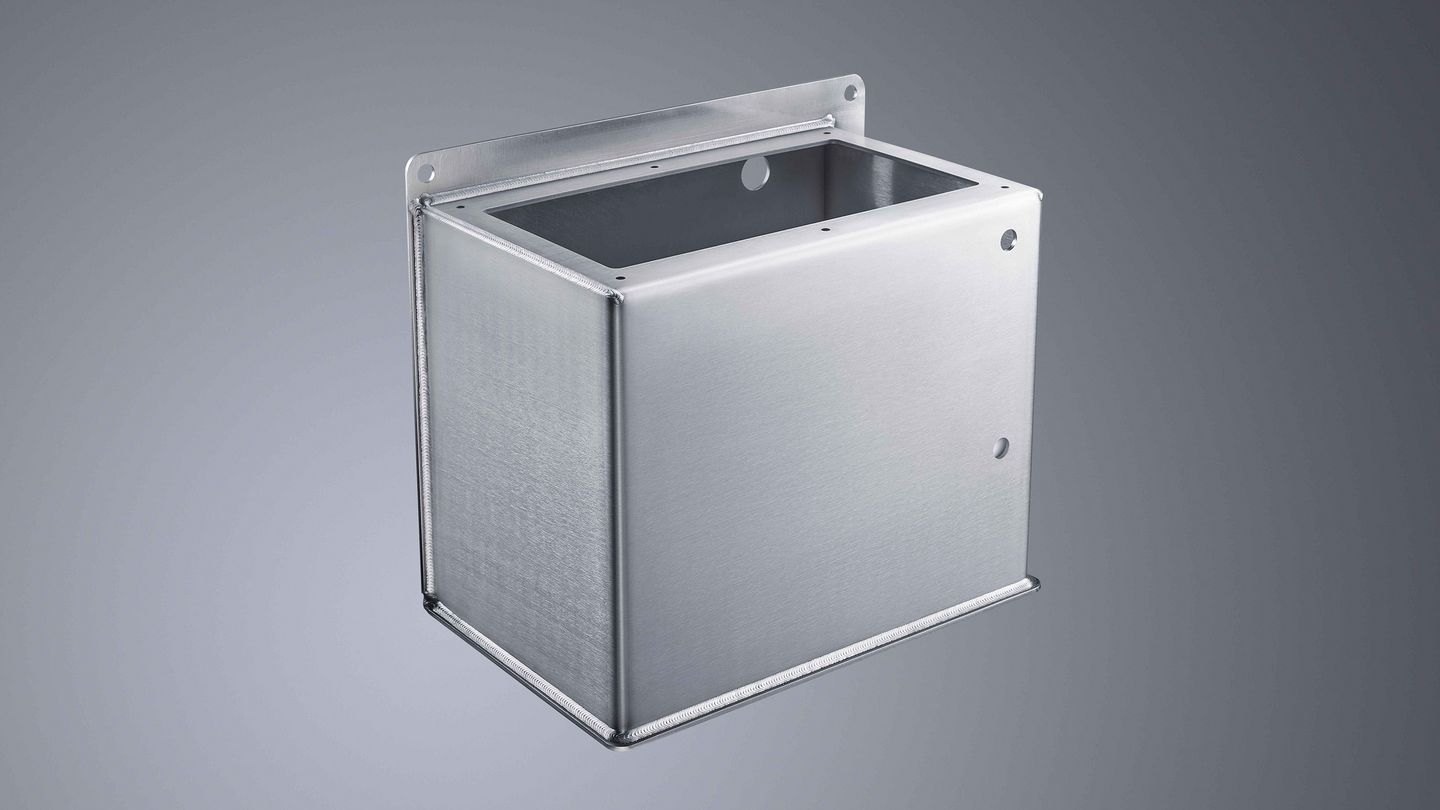
Technical basis of arc welding (MIG/MAG welding)
During arc welding, the high temperature required for welding is generated by an electric current: to do so, voltage is applied to the workpiece and the welding wire (electrode), creating an arc between these two poles. This creates a melt along the join connection of the workpiece. During MIG/MAG welding, the welding wire is continuously fed into the process and continuously melts. A shielding gas is also used to prevent oxygen getting to the weld seam. These arc welding procedures are therefore also called gas shielded metal arc welding procedures.